Docker Containerization Guidelines#
Important
By default, all Docker containers are pre-configured and ready to use.
The editable development version of scikit-plots is already installed,
so you can verify the installation immediately by running:
scikitplot -V
Important
Once the Docker environment is ready to use, you can proceed to the quickstart section to verify the build:
See also
🐋 Docker Containerization#
💡 Work on Docker Desktop or Github Codespaces
Here’s how containerization works:
Isolation: Containers run independently of each other and the host system, ensuring that they don’t interfere with other applications or containers.
Portability: Since containers include everything the application needs to run, they can be moved between different environments (like from development to production) without any compatibility issues.
Efficiency: Containers are more lightweight than virtual machines (VMs) because they share the host OS’s kernel rather than running their own separate operating system. This makes them faster and more resource-efficient.
Consistency: The application inside the container runs the same way regardless of where it’s deployed, ensuring consistency across environments.
🏷️ Github Codespaces Guide#
(Connect IDE Interface Vscode or Jupyter Notebook)
👉 (recommended) Choose (recommended) not (default) Option for best practise:
Step by step:
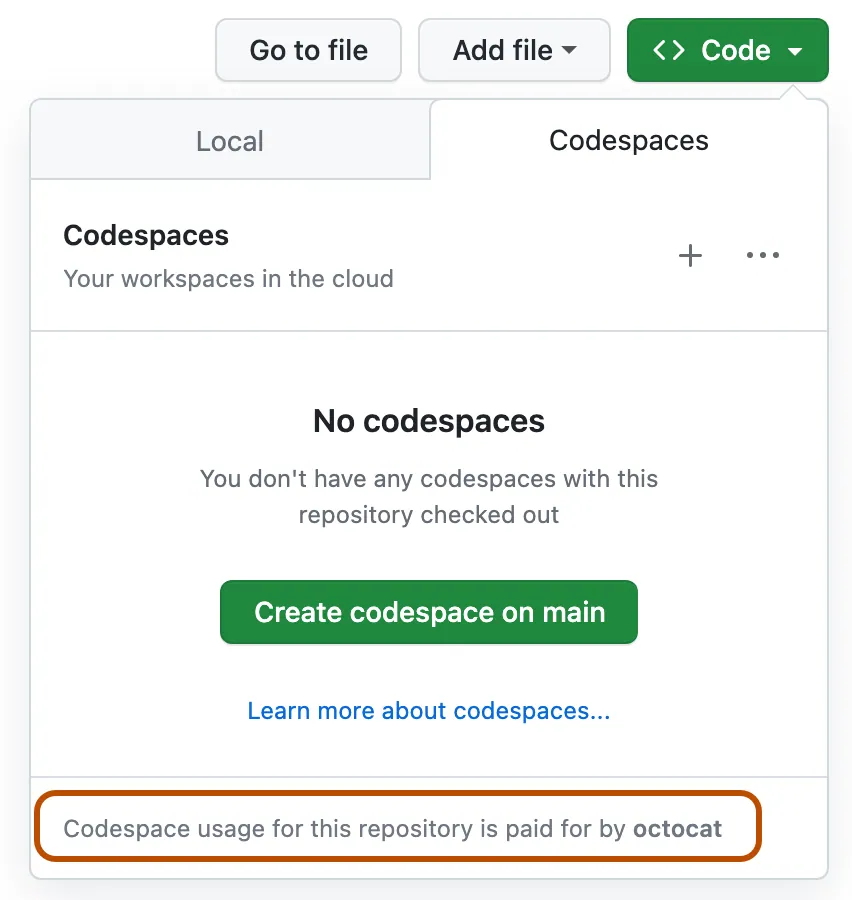
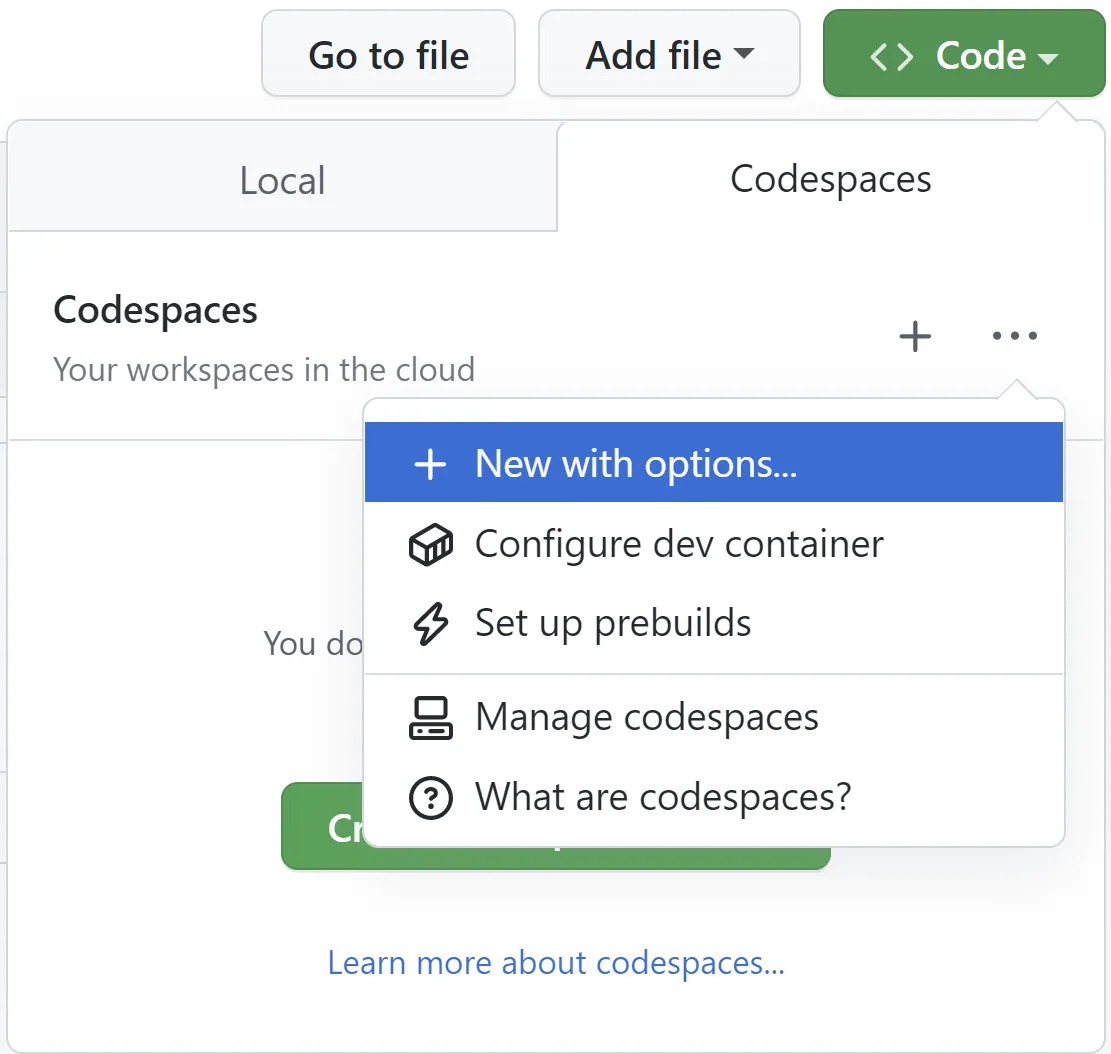
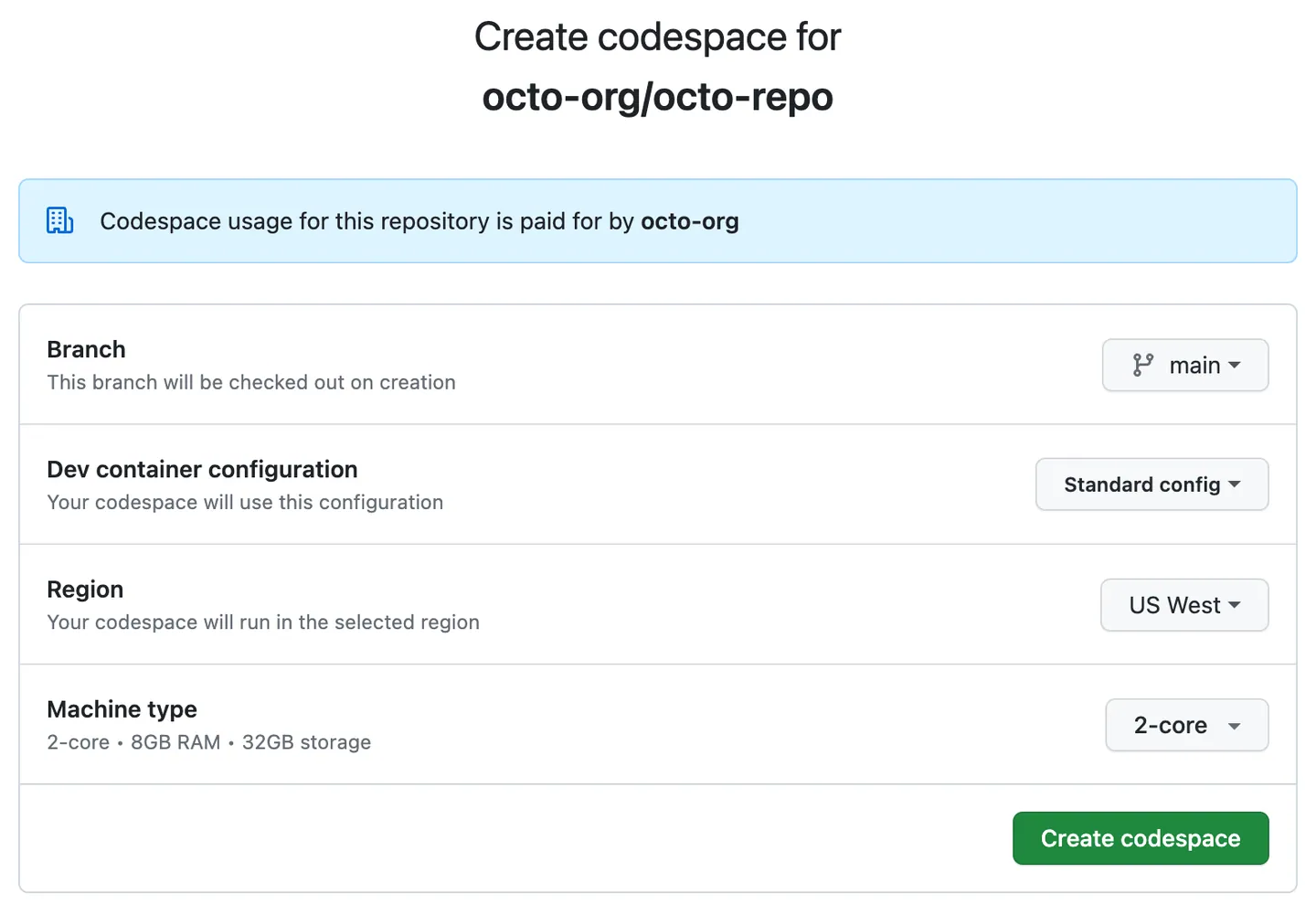
🏷️ Docker Desktop Guide#
## Forked repo: https://github.com/scikit-plots/scikit-plots.git
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USER-NAME/scikit-plots.git
cd scikit-plots/docker
## Use terminal or open to vscode to run ``docker compose``
code .
Docker Environment Setup for IDE (Vscode/Jupyter) and/or NVIDIA GPU driver
This repository contains Docker & Docker Compose configurations for running Jupyter Notebooks with optional NVIDIA GPU support.
You can run containers with either host-installed CUDA or pre-installed CUDA inside the container.
🐳 Docker Compose Quickstart Guide#
(Optionally) 📦 Prebuilt Image from Docker Hub#
See also
You can use the prebuilt image directly from Docker Hub:
📄 Docker Hub: hub.docker.com/r/scikitplot/scikit-plots
# docker pull scikitplot/scikit-plots
docker run -it --rm scikitplot/scikit-plots bash
🏷️ Using Docker Compose: The easiest way to launch the environment.#
▶️ Run Docker Env Jupyter Notebook (CPU only)
docker compose up --build scikit-plots_latest-jupyter
▶️ Run Docker Env Jupyter Notebook (With NVIDIA Host GPU)
docker compose up --build app_nvidia_host_gpu_driver
▶️ Run Docker Env Jupyter Notebook (With NVIDIA Internal CUDA GPU)
docker compose up --build app_nvidia_internal_gpu_driver
▶️ Run Docker Env Jupyter Notebook by VS Code#
▶️ Connect Docker Container Especially When Docker-GUI dont available#
# docker-compose up --build scikit-plots_latest-jupyter
docker ps # check running containers
docker logs CONTAINER_ID_OR_NAME # find jupyter (token) http address 127.0....
docker exec -it CONTAINER_ID_OR_NAME bash # Connect interactive terminal
▶️ Run setup_vscode_extensions.sh#
## (Optionally) Install common vscode extensions
##✅ C/C++/Python and Jupyter Notebook
##✅ Linter and Formatter
bash docker/scripts/setup_vscode_extensions.sh # (not needed every time)
▶️ Run post_create_commands.sh#
“See Also: bash-first-run-notice.txt”
bash-first-run-notice.txt#
👋 Welcome to the `scikit-plots` Dev Environment (Docker / Codespaces)
🧭 Quick Navigation:
• 🔎 Open the Command Palette → `Ctrl+Shift+P` / `Cmd+Shift+P` or `F1`
• 📘 Quick Start → https://scikit-plots.github.io/dev/introduction/quick_start.html
• 🛠️ Dev Guide → https://scikit-plots.github.io/dev/devel/index.html
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
⭐ 🌟 IMPORTANT: Complete Environment Setup
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
✅ Check Installation:
$ python -c "import scikitplot; scikitplot.show_config()"
$ scikitplot -V
✅ Post-Create Setup All-In-One Script (Recommended):
$ bash docker/scripts/all_post_create.sh
✅ Git Safe Configs:
$ # bash docker/scripts/git_add_safe_dirs.sh # add safe directories for git
$ git config --global --add safe.directory '*'
✅ (Optionally) Git Submodules Clone/Download/Initialize Configs, Not Needed Every Time:
$ git submodule update --init
$ git submodule update --init --recursive
✅ Git Upstream Configs:
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/scikit-plots/scikit-plots.git
✅ Git Tag Configs:
$ git fetch upstream --tags
✅ Create Environment (Conda/Mamba/Micromamba):
$ conda create -n py311 python=3.11 ipykernel -y
$ conda activate py311
✅ Install Build Dependencies:
$ pip install -r requirements/build.txt
$ pip install -r requirements/all.txt
✅ (Optional) Install CPU-specific packages:
$ pip install -r requirements/cpu.txt
✅ Git hooks manager Initialize, Ensures code meets quality standards before it
$ pre-commit install
✅ Install the current package in editable mode, using the current environment for building, and ignore cached builds:
$ pip install --no-build-isolation --no-cache-dir -e . -vvv
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
📦 Environment Management Notes (Conda/Anaconda/Miniconda/Miniforge/Mamba/Micromamba):
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
• Initialize Conda shell support (if needed):
# https://mamba.readthedocs.io/en/latest/installation/micromamba-installation.html
$ micromamba shell init --shell bash
$ mamba init
$ conda init
• See environments:
$ micromamba info -e
$ mamba info -e
$ conda info -e
• Activate environments (depending on tool):
$ micromamba activate $(micromamba info -e | grep py312)
$ micromamba activate /root/micromamba/envs/py312
$ micromamba activate py311
$ conda activate py311
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
💡 Troubleshooting:
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
• 💽 Disk Space:
$ df -h && du -h --max-depth=1
• 💾 Creation logs (Codespaces):
⚠️ 👇 Check Codespace Container creation raise `ERROR: ... : No space left on device`
$ cat /workspaces/.codespaces/.persistedshare/creation.log
• 📦 Warning: Clock skew detected. Your build may be incomplete (Mostly fixed; closed all open files.):
⚠️ Issues mostly fixed by closing all currently open files.
⚠️ ⏻ Restart Computer, If Needed.
$ make clean
$ find . -exec touch {} +
$ python -m pip install --no-build-isolation --no-cache-dir -e . -v
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
✍ Starting Development
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🌿 Create a new branch before working:
$ git checkout -b feature/my-new-feature
✍ Proceed to create a branch if you have uncommitted changes and are beginning work on a new feature or bug fix.
🔄 Read more: https://scikit-plots.github.io/dev/devel/quickstart_contributing.html#creating-a-branch
🚯 Stop Containers#
docker compose down
🐳 Docker Compose Configuration#
This project is based on Docker Compose and includes multiple services:
🔹 scikit-plots_latest-jupyter (CPU-Only)
Runs Jupyter Notebook using jupyter/tensorflow-notebook:latest
No CUDA support, best for lightweight tasks
Mounts the local folder scikit-plots to /home/jovyan/work
Runs on port 8888
🔹 app_nvidia_host_gpu_driver (Uses Host CUDA)
Runs Jupyter Notebook using jupyter/tensorflow-notebook:latest
Uses host-installed CUDA for GPU acceleration
Requires NVIDIA runtime enabled (–runtime=nvidia)
Runs on port 8889
🔹 app_nvidia_internal_gpu_driver (CUDA Inside Container)
Runs nvidia/cuda:12.6.3-cudnn-runtime-ubuntu24.04 with pre-installed CUDA
Includes NVIDIA GPU support without needing host CUDA
Requires NVIDIA runtime (–runtime=nvidia)
Runs on port 8890
🛠️ Custom Docker Commands#
If you need more control, you can use Docker CLI commands.
▶️ Build & Run the Container Manually
docker build -t my-custom-container -f docker/Dockerfile .
docker run -it --rm -p 8888:8888 my-custom-container
▶️ Check GPU Availability Inside Container
docker exec -it <container_id> nvidia-smi
📂 Folder Structure#
docker/
├── docker-compose.yml # Primary Docker Compose file
├── docker-compose.override.yml # Optional override file (auto-included if present)
├── Dockerfile # Custom Dockerfile
├── scripts/
│ ├── install_gpu_nvidia_cuda.sh # GPU setup scripts
🖥️ Useful References#
📚 Jupyter Docker Stacks: Read the Docs
📚 Docker Compose: Official Docs
📚 LocalStack Installation with Docker Compose
📚 NVIDIA CUDA in Containers: NVIDIA Docs

🚀 Now you’re ready to run Jupyter notebooks in Docker! 😊