annoy.Index python-api with examples#
An example showing the Index class.
See also
import numpy as np
import random; random.seed(0)
# from annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex
# from scikitplot.cexternals._annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex
from scikitplot.annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex, Index
print(Annoy.__doc__)
Compiled with GCC/Clang. Using 512-bit AVX instructions.
Approximate Nearest Neighbors index (Annoy) with a small, lazy C-extension wrapper.
::
>>> Annoy(
>>> f=None,
>>> metric=None,
>>> *,
>>> n_neighbors=5,
>>> on_disk_path=None,
>>> prefault=None,
>>> seed=None,
>>> verbose=None,
>>> schema_version=None,
>>> )
Parameters
----------
f : int or None, optional, default=None
Vector dimension. If ``0`` or ``None``, dimension may be inferred from the
first vector passed to ``add_item`` (lazy mode).
If None, treated as ``0`` (reset to default).
metric : {"angular", "cosine", "euclidean", "l2", "lstsq", "manhattan", "l1", "cityblock", "taxicab", "dot", "@", ".", "dotproduct", "inner", "innerproduct", "hamming"} or None, optional, default=None
Distance metric (one of 'angular', 'euclidean', 'manhattan', 'dot', 'hamming').
If omitted and ``f > 0``, defaults to ``'angular'`` (cosine-like).
If omitted and ``f == 0``, metric may be set later before construction.
If None, behavior depends on ``f``:
* If ``f > 0``: defaults to ``'angular'`` (legacy behavior; may emit a
:class:`FutureWarning`).
* If ``f == 0``: leaves the metric unset (lazy). You may set
:attr:`metric` later before construction, or it will default to
``'angular'`` on first :meth:`add_item`.
n_neighbors : int, default=5
Non-negative integer Number of neighbors to retrieve for each query.
on_disk_path : str or None, optional, default=None
If provided, configures the path for on-disk building. When the underlying
index exists, this enables on-disk build mode (equivalent to calling
:meth:`on_disk_build` with the same filename).
Note: Annoy core truncates the target file when enabling on-disk build.
This wrapper treats ``on_disk_path`` as strictly equivalent to calling
:meth:`on_disk_build` with the same filename (truncate allowed).
In lazy mode (``f==0`` and/or ``metric is None``), activation occurs once
the underlying C++ index is created.
prefault : bool or None, optional, default=None
If True, request page-faulting index pages into memory when loading
(when supported by the underlying platform/backing).
If None, treated as ``False`` (reset to default).
seed : int or None, optional, default=None
Non-negative integer seed. If set before the index is constructed,
the seed is stored and applied when the C++ index is created.
Seed value ``0`` is treated as \"use Annoy's deterministic default seed\"
(a :class:`UserWarning` is emitted when ``0`` is explicitly provided).
verbose : int or None, optional, default=None
Verbosity level. Values are clamped to the range ``[-2, 2]``.
``level >= 1`` enables Annoy's verbose logging; ``level <= 0`` disables it.
Logging level inspired by gradient-boosting libraries:
* ``<= 0`` : quiet (warnings only)
* ``1`` : info (Annoy's ``verbose=True``)
* ``>= 2`` : debug (currently same as info, reserved for future use)
schema_version : int, optional, default=None
Serialization/compatibility strategy marker.
This does not change the Annoy on-disk format, but it *does* control
how the index is snapshotted in pickles.
* ``0`` or ``1``: pickle stores a ``portable-v1`` snapshot (fast restore,
ABI-checked).
* ``2``: pickle stores ``canonical-v1`` (portable across ABIs; restores by
rebuilding deterministically).
* ``>=3``: pickle stores both portable and canonical (canonical is used as
a fallback if the ABI check fails).
If None, treated as ``0`` (reset to default).
Attributes
----------
f : int, default=0
Vector dimension. ``0`` means "unknown / lazy".
metric : {'angular', 'euclidean', 'manhattan', 'dot', 'hamming'}, default="angular"
Canonical metric name, or None if not configured yet (lazy).
n_neighbors : int, default=5
Non-negative integer Number of neighbors to retrieve for each query.
on_disk_path : str or None, optional, default=None
Configured on-disk build path. Setting this attribute enables on-disk
build mode (equivalent to :meth:`on_disk_build`), with safety checks
to avoid implicit truncation of existing files.
prefault : bool, default=False
Stored prefault flag (see :meth:`load`/`:meth:`save` prefault parameters).
seed : int or None, optional, default=None
Non-negative integer seed. Also provides :meth:`random_state`
verbose : int or None, optional, default=None
Verbosity level.
schema_version : int, default=0
Reserved schema/version marker (stored; does not affect on-disk format).
n_features : int
Alias of :meth:`f` (dimension), provided for scikit-learn naming parity.
Also provides :meth:`n_features_`, :meth:`n_features_in_`.
n_features_out_ : int
Number of output features produced by transform.
feature_names_in_ : list-like
Input feature names seen during fit.
Set only when explicitly provided via fit(..., feature_names=...).
y : list-like | None, optional, default=None
Dense label cache aligned to item ids (``0 .. n_items-1``). This is a
convenience view for scikit-learn style APIs and may be derived from
``y_map`` lazily.
The setter accepts sequences only (a dict is not allowed); when possible it
validates that ``len(y) == n_items`` and updates ``y_map`` deterministically.
y_map : dict | None, optional, default=None
Canonical sparse mapping ``{item_id -> label}``. Keys must be non-negative
integers and (when an index exists) strictly less than ``n_items``.
Setting this property invalidates the dense ``y`` cache; ``y`` is
materialized lazily (missing keys become ``None``).
See Also
--------
add_item : Add a vector to the index.
build : Build the forest after adding items.
unbuild : Remove trees to allow adding more items.
get_nns_by_item, get_nns_by_vector : Query nearest neighbours.
save, load : Persist the index to/from disk.
serialize, deserialize : Persist the index to/from bytes.
set_seed : Set the random seed deterministically.
set_verbose : Set verbosity level.
info : Return a structured summary of the current index.
Notes
-----
* Once the underlying C++ index is created, ``f`` and ``metric`` are immutable.
This keeps the object consistent and avoids undefined behavior.
* The C++ index is created lazily when sufficient information is available:
when both ``f > 0`` and ``metric`` are known, or when an operation that
requires the index is first executed.
* If ``f == 0``, the dimensionality is inferred from the first non-empty vector
passed to :meth:`add_item` and is then fixed for the lifetime of the index.
* Assigning ``None`` to :attr:`f` is not supported. Use ``0`` for lazy
inference (this matches ``Annoy(f=None, ...)`` at construction time).
* If ``metric`` is omitted while ``f > 0``, the current behavior defaults to
``'angular'`` and may emit a :class:`FutureWarning`. To avoid warnings and
future behavior changes, always pass ``metric=...`` explicitly.
* Items must be added *before* calling :meth:`build`. After :meth:`build`, the
index becomes read-only; to add more items, call :meth:`unbuild`, add items
again with :meth:`add_item`, then call :meth:`build` again.
* Very large indexes can be built directly on disk with :meth:`on_disk_build`
and then memory-mapped with :meth:`load`.
* :meth:`info` returns a structured summary (dimension, metric, counts, and
optional memory usage) suitable for programmatic inspection.
* This wrapper stores user configuration (e.g., seed/verbosity) even before the
C++ index exists and applies it deterministically upon construction.
Developer Notes:
- Source of truth:
* ``f`` (int) and ``metric_id`` (enum) describe configuration.
* ``ptr`` is NULL when index is not constructed.
- Invariant:
* ``ptr != NULL`` implies ``f > 0`` and ``metric_id != METRIC_UNKNOWN``.
Examples
--------
>>> from annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex
High-level API:
>>> from scikitplot.cexternals._annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex
>>> from scikitplot.annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex, Index
The lifecycle follows the examples in ``test.ipynb``:
1. **Construct the index**
>>> import random; random.seed(0)
>>> # from annoy import AnnoyIndex
>>> from scikitplot.cexternals._annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex
>>> from scikitplot.annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex, Index
>>> idx = Annoy(f=3, metric="angular")
>>> idx.f, idx.metric
(3, 'angular')
If you pass ``f=0`` the dimension can be inferred on the first
call to :meth:`add_item`.
2. **Add items**
>>> idx.add_item(0, [1.0, 0.0, 0.0])
>>> idx.add_item(1, [0.0, 1.0, 0.0])
>>> idx.add_item(2, [0.0, 0.0, 1.0])
>>> idx.get_n_items()
3
3. **Build the forest**
>>> idx.build(n_trees=-1)
>>> idx.get_n_trees()
10
>>> idx.memory_usage() # byte
543076
After :meth:`build` the index becomes read-only. You can still
query, save, load and serialize it.
4. **Query neighbours**
By stored item id:
>>> idx.get_nns_by_item(0, 5)
[0, 1, 2, ...]
With distances:
>>> idx.get_nns_by_item(0, 5, include_distances=True)
([0, 1, 2, ...], [0.0, 1.22, 1.26, ...])
Or by an explicit query vector:
>>> idx.get_nns_by_vector([0.1, 0.2, 0.3], 5, include_distances=True)
([103, 71, 160, 573, 672], [...])
5. **Persistence**
To work with memory-mapped indices on disk:
>>> idx.save("annoy_test.annoy")
>>> idx2 = Annoy(f=100, metric="angular")
>>> idx2.load("annoy_test.annoy")
>>> idx2.get_n_items()
1000
Or via raw byte:
>>> buf = idx.serialize()
>>> new_idx = Annoy(f=100, metric="angular")
>>> new_idx.deserialize(buf)
>>> new_idx.get_n_items()
1000
You can release OS resources with :meth:`unload` and drop the
current forest with :meth:`unbuild`.
print(Index.__doc__)
High-level ANNoy index composed from mixins.
Parameters
----------
f : int or None, optional, default=None
Vector dimension. If ``0`` or ``None``, dimension may be inferred from the
first vector passed to ``add_item`` (lazy mode).
If None, treated as ``0`` (reset to default).
metric : {"angular", "cosine", "euclidean", "l2", "lstsq", "manhattan", "l1", "cityblock", "taxicab", "dot", "@", ".", "dotproduct", "inner", "innerproduct", "hamming"} or None, optional, default=None
Distance metric (one of 'angular', 'euclidean', 'manhattan', 'dot', 'hamming').
If omitted and ``f > 0``, defaults to ``'angular'`` (cosine-like).
If omitted and ``f == 0``, metric may be set later before construction.
If None, behavior depends on ``f``:
* If ``f > 0``: defaults to ``'angular'`` (legacy behavior; may emit a
:class:`FutureWarning`).
* If ``f == 0``: leaves the metric unset (lazy). You may set
:attr:`metric` later before construction, or it will default to
``'angular'`` on first :meth:`add_item`.
n_neighbors : int, default=5
Non-negative integer Number of neighbors to retrieve for each query.
on_disk_path : str or None, optional, default=None
If provided, configures the path for on-disk building. When the underlying
index exists, this enables on-disk build mode (equivalent to calling
:meth:`on_disk_build` with the same filename).
Note: Annoy core truncates the target file when enabling on-disk build.
This wrapper treats ``on_disk_path`` as strictly equivalent to calling
:meth:`on_disk_build` with the same filename (truncate allowed).
In lazy mode (``f==0`` and/or ``metric is None``), activation occurs once
the underlying C++ index is created.
prefault : bool or None, optional, default=None
If True, request page-faulting index pages into memory when loading
(when supported by the underlying platform/backing).
If None, treated as ``False`` (reset to default).
seed : int or None, optional, default=None
Non-negative integer seed. If set before the index is constructed,
the seed is stored and applied when the C++ index is created.
Seed value ``0`` is treated as "use Annoy's deterministic default seed"
(a :class:`UserWarning` is emitted when ``0`` is explicitly provided).
verbose : int or None, optional, default=None
Verbosity level. Values are clamped to the range ``[-2, 2]``.
``level >= 1`` enables Annoy's verbose logging; ``level <= 0`` disables it.
Logging level inspired by gradient-boosting libraries:
* ``<= 0`` : quiet (warnings only)
* ``1`` : info (Annoy's ``verbose=True``)
* ``>= 2`` : debug (currently same as info, reserved for future use)
schema_version : int, optional, default=None
Serialization/compatibility strategy marker.
This does not change the Annoy on-disk format, but it *does* control
how the index is snapshotted in pickles.
* ``0`` or ``1``: pickle stores a ``portable-v1`` snapshot (fast restore,
ABI-checked).
* ``2``: pickle stores ``canonical-v1`` (portable across ABIs; restores by
rebuilding deterministically).
* ``>=3``: pickle stores both portable and canonical (canonical is used as
a fallback if the ABI check fails).
If None, treated as ``0`` (reset to default).
Attributes
----------
f : int, default=0
Vector dimension. ``0`` means "unknown / lazy".
metric : {'angular', 'euclidean', 'manhattan', 'dot', 'hamming'}, default="angular"
Canonical metric name, or None if not configured yet (lazy).
n_neighbors : int, default=5
Non-negative integer Number of neighbors to retrieve for each query.
on_disk_path : str or None, optional, default=None
Configured on-disk build path. Setting this attribute enables on-disk
build mode (equivalent to :meth:`on_disk_build`), with safety checks
to avoid implicit truncation of existing files.
seed, random_state : int or None, optional, default=None
Non-negative integer seed.
verbose : int or None, optional, default=None
Verbosity level.
prefault : bool, default=False
Stored prefault flag (see :meth:`load`/`:meth:`save` prefault parameters).
schema_version : int, default=0
Reserved schema/version marker (stored; does not affect on-disk format).
n_features, n_features_, n_features_in_ : int
Alias of `f` (dimension), provided for scikit-learn naming parity.
n_features_out_ : int
Number of output features produced by transform.
feature_names_in_ : list-like
Input feature names seen during fit.
Set only when explicitly provided via fit(..., feature_names=...).
y : dict | None, optional, default=None
If provided to fit(X, y), labels are stored here after a successful build.
You may also set this property manually. When possible, the setter enforces
that len(y) matches the current number of items (n_items).
pickle_mode : PickleMode
Pickle strategy used by :class:`~scikitplot.annoy._mixins._pickle.PickleMixin`.
compress_mode : CompressMode or None
Optional compression used by :class:`~scikitplot.annoy._mixins._pickle.PickleMixin`
when serializing to bytes.
Notes
-----
This class is a direct subclass of the C-extension backend. It does not
override ``__new__`` and does not rely on cooperative initialization across
mixins. Mixins must be written so that their methods work even if they
define no ``__init__`` at all.
See Also
--------
scikitplot.cexternals._annoy.Annoy
Index.from_low_level
from scikitplot import annoy
annoy.__version__, dir(annoy), dir(annoy.Annoy)
('2.0.0+git.20251130.8a7e82cb537053926b0ac6ec132b9ccc875af40c', ['Annoy', 'AnnoyIndex', 'CompressMode', 'Index', 'IndexIOMixin', 'MetaMixin', 'NDArrayMixin', 'PickleMixin', 'PickleMode', 'PlottingMixin', 'VectorOpsMixin', '__all__', '__author__', '__author_email__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__git_hash__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__', '__spec__', '__version__', '_base', '_metadata', '_mixins', '_utils', 'annotations', 'annoylib'], ['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__sklearn_clone__', '__sklearn_is_fitted__', '__sklearn_tags__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '_f', '_metric_id', '_on_disk_path', '_prefault', '_repr_html_', '_schema_version', '_y', '_y_map', 'add_item', 'build', 'deserialize', 'f', 'feature_names_in_', 'fit', 'fit_transform', 'get_distance', 'get_feature_names_out', 'get_item_vector', 'get_n_items', 'get_n_trees', 'get_nns_by_item', 'get_nns_by_vector', 'get_params', 'info', 'load', 'memory_usage', 'metric', 'n_features', 'n_features_', 'n_features_in_', 'n_features_out_', 'n_neighbors', 'on_disk_build', 'on_disk_path', 'prefault', 'random_state', 'rebuild', 'repr_info', 'save', 'schema_version', 'seed', 'serialize', 'set_params', 'set_seed', 'set_verbose', 'set_verbosity', 'transform', 'unbuild', 'unload', 'verbose', 'y', 'y_map'])
import sys
# TODO: change this import to wherever your modified AnnoyIndex lives
# e.g. scikitplot.cexternals._annoy or similar
# import scikitplot.cexternals._annoy as annoy
from scikitplot import annoy
sys.modules["annoy"] = annoy # now `import annoy` will resolve to your module
import annoy
print(annoy.__doc__)
Public Annoy Python API for scikitplot.
Spotify ANNoy [1]_ (Approximate Nearest Neighbors Oh Yeah).
This package exposes **two layers**:
Exports:
1. Low-level C-extension types copied from Spotify's *annoy* project:
:class:`~scikitplot.cexternals._annoy.Annoy` and :class:`~scikitplot.cexternals._annoy.AnnoyIndex`.
2. A high-level, mixin-composed wrapper :class:`~scikitplot.annoy.Index` that:
- forwards the complete low-level API deterministically,
- adds versioned manifest import/export,
- provides explicit index I/O names (``save_index`` / ``load_index``),
- provides safe Python-object persistence helpers (pickling),
- adds optional NumPy export and plotting utilities.
Notes
-----
This module intentionally avoids side effects at import time (no implicit NumPy
or matplotlib imports).
.. seealso::
* :ref:`ANNoy <annoy-index>`
* :ref:`cexternals/ANNoy <cexternals-annoy-index>`
* https://github.com/spotify/annoy
* https://pypi.org/project/annoy
See Also
--------
scikitplot.cexternals._annoy
Low-level C-extension backend.
scikitplot.annoy.Index
High-level wrapper composed from mixins.
References
----------
.. [1] `Spotify AB. (2013, Feb 20). "ANNoy: Approximate Nearest Neighbors Oh Yeah"
Github. https://github.com/spotify/annoy <https://github.com/spotify/annoy>`_
Examples
--------
>>> import random
>>> random.seed(0)
>>> # from annoy import AnnoyIndex
>>> from scikitplot.cexternals._annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex
>>> from scikitplot.annoy import Annoy, AnnoyIndex, Index
>>> f = 40 # vector dimensionality
>>> t = Index(f, "angular") # same constructor as the low-level backend
>>> t.add_item(0, [1] * f)
>>> t.build(10) # Build 10 trees
>>> t.get_nns_by_item(0, 1) # Find nearest neighbor
Index()
# =============================================================
# 1. Construction
# =============================================================
idx = Index()
idx = Index(None, None)
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
print(type(idx))
idx
# help(idx.info)
Index dimension: 0
Metric : None
{'f': 0, 'metric': None, 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 0, 'n_trees': 0}
Annoy(**{'f': 0, 'metric': None, 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
<class 'scikitplot.annoy._base.Index'>
dir(idx)
['_META_SCHEMA_VERSION', '_PICKLE_STATE_VERSION', '__annotations__', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__sklearn_clone__', '__sklearn_is_fitted__', '__sklearn_tags__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_as_2d_coords', '_backend', '_compress_mode', '_f', '_get_lock', '_lock', '_metric_id', '_ndarray_expected_rows', '_ndarray_infer_f', '_ndarray_iter_ids', '_ndarray_materialize_dense', '_ndarray_require_unbuilt', '_on_disk_path', '_pickle_mode', '_plotting_backend', '_prefault', '_rebuild', '_repr_html_', '_schema_version', '_y', '_y_map', 'add_item', 'add_items', 'backend', 'build', 'compress_mode', 'deserialize', 'f', 'feature_names_in_', 'fit', 'fit_transform', 'from_bytes', 'from_json', 'from_low_level', 'from_metadata', 'from_yaml', 'get_distance', 'get_feature_names_out', 'get_item_vector', 'get_item_vectors', 'get_n_items', 'get_n_trees', 'get_nns_by_item', 'get_nns_by_vector', 'get_params', 'info', 'iter_item_vectors', 'kneighbors', 'kneighbors_graph', 'load', 'load_bundle', 'load_index', 'memory_usage', 'metric', 'n_features', 'n_features_', 'n_features_in_', 'n_features_out_', 'n_neighbors', 'on_disk_build', 'on_disk_path', 'pickle_mode', 'plot_index', 'plot_knn_edges', 'prefault', 'query_by_item', 'query_by_vector', 'query_vectors_by_item', 'query_vectors_by_vector', 'random_state', 'rebuild', 'repr_info', 'save', 'save_bundle', 'save_index', 'schema_version', 'seed', 'serialize', 'set_params', 'set_seed', 'set_verbose', 'set_verbosity', 'to_bytes', 'to_json', 'to_metadata', 'to_numpy', 'to_pandas', 'to_scipy_csr', 'to_yaml', 'transform', 'unbuild', 'unload', 'verbose', 'y', 'y_map']
# AttributeError: readonly attribute
# idx._metric_id = 1
idx._f, idx._metric_id, idx._on_disk_path
(0, 0, None)
idx.f, idx.metric, idx.on_disk_path
(0, None, None)
idx.metric = "dot"
idx
idx.f, idx.metric, idx.on_disk_path
(0, 'dot', None)
type(idx)
# =============================================================
# 1. Construction
# =============================================================
idx = Index(f=3, metric="angular")
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
Index dimension: 3
Metric : angular
{'f': 3, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 0, 'n_trees': 0}
Annoy(**{'f': 3, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# =============================================================
# 2. Add items
# =============================================================
idx.add_item(0, [0, 0, 0])
idx.add_item(1, [1, 0, 0])
idx.add_item(2, [0, 1, 0])
idx.add_item(3, [0, 0, 1])
idx.add_item(4, [2, 0, 0])
idx.add_item(5, [0, 2, 0])
idx.add_item(6, [0, 0, 2])
idx.add_item(7, [3, 0, 0])
idx.add_item(8, [0, 3, 0])
idx.add_item(9, [0, 0, 3])
idx.add_item(10, [4, 0, 0])
idx.add_item(11, [0, 4, 0])
idx.add_item(12, [0, 0, 4])
idx.add_item(12, [4, 0, 0])
idx.add_item(13, [0, 4, 0])
idx.add_item(14, [0, 0, 4])
print("Number of items:", idx.get_n_items())
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
Number of items: 15
Index dimension: 3
Metric : angular
{'f': 3, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 15, 'n_trees': 0}
Annoy(**{'f': 3, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
def plot(idx, y=None, **kwargs):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scikitplot.cexternals._annoy._plotting as utils
single = np.zeros(idx.get_n_items(), dtype=int)
if y is None:
double = np.random.uniform(0, 1, idx.get_n_items()).round()
# single vs double
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(12, 5))
alpha = kwargs.pop("alpha", 0.8)
y2 = utils.plot_annoy_index(
idx,
dims = list(range(idx.f)),
plot_kwargs={"draw_legend": False},
ax=ax[0],
)[0]
utils.plot_annoy_knn_edges(
idx,
y2,
k=1,
line_kwargs={"alpha": alpha},
ax=ax[1],
)
idx.unbuild()
idx.build(100)
plot(idx)
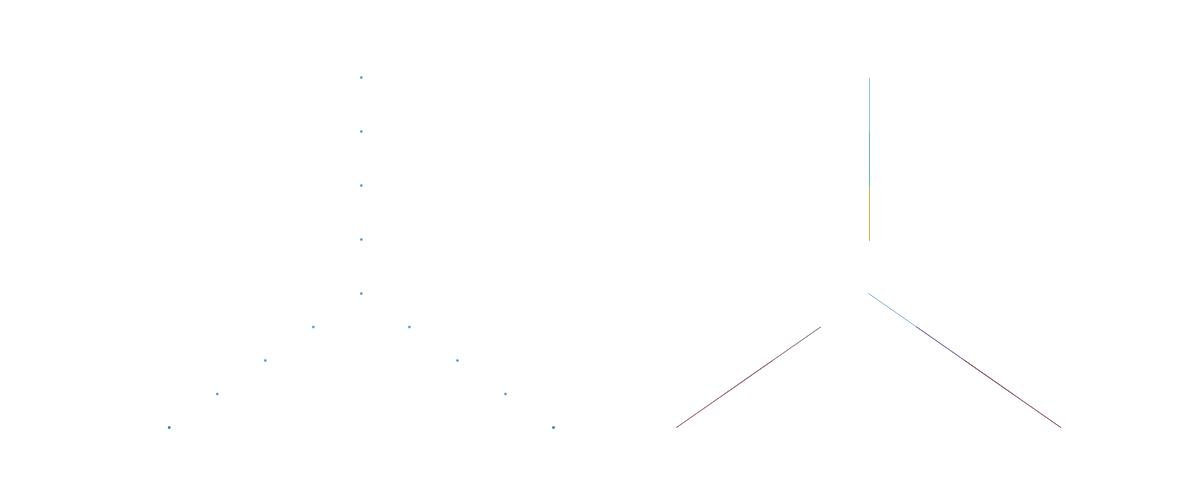
from scikitplot import annoy as a
print(a.Annoy) # same
print(a.AnnoyIndex) # same
print(a.Index) # should show <class '..._base.Index'>
print(isinstance(idx, a.Annoy))
print(isinstance(idx, a.AnnoyIndex))
print(isinstance(idx, a.Index))
print(type(idx))
print(idx.__class__.__module__)
print(idx.__class__.__mro__)
<class 'scikitplot.cexternals._annoy.Annoy'>
<class 'scikitplot.cexternals._annoy.Annoy'>
<class 'scikitplot.annoy._base.Index'>
True
True
True
<class 'scikitplot.annoy._base.Index'>
scikitplot.annoy._base
(<class 'scikitplot.annoy._base.Index'>, <class 'scikitplot.cexternals._annoy.Annoy'>, <class 'scikitplot.annoy._mixins._meta.MetaMixin'>, <class 'scikitplot.annoy._mixins._io.IndexIOMixin'>, <class 'scikitplot.annoy._mixins._pickle.PickleMixin'>, <class 'scikitplot.annoy._mixins._vectors.VectorOpsMixin'>, <class 'scikitplot.annoy._mixins._ndarray.NDArrayMixin'>, <class 'scikitplot.annoy._mixins._plotting.PlottingMixin'>, <class 'object'>)
# =============================================================
# 1. Construction
# =============================================================
idx = Index(f=3, metric="angular")
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
Index dimension: 3
Metric : angular
{'f': 3, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 0, 'n_trees': 0}
Annoy(**{'f': 3, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# =============================================================
# 2. Add items
# =============================================================
idx.add_item(0, [1, 0, 0])
idx.add_item(1, [0, 1, 0])
idx.add_item(2, [0, 0, 1])
print("Number of items:", idx.get_n_items())
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
Number of items: 3
Index dimension: 3
Metric : angular
# =============================================================
# 1. Construction
# =============================================================
idx = Index(100, metric="angular")
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
idx.on_disk_build("annoy_test_2.annoy")
# help(idx.on_disk_build)
Index dimension: 100
Metric : angular
# =============================================================
# 2. Add items
# =============================================================
f=100
n=1000
for i in range(n):
if(i % (n//10) == 0): print(f"{i} / {n} = {1.0 * i / n}")
# v = []
# for z in range(f):
# v.append(random.gauss(0, 1))
v = [random.gauss(0, 1) for _ in range(f)]
idx.add_item(i, v)
print("Number of items:", idx.get_n_items())
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
print(idx)
0 / 1000 = 0.0
100 / 1000 = 0.1
200 / 1000 = 0.2
300 / 1000 = 0.3
400 / 1000 = 0.4
500 / 1000 = 0.5
600 / 1000 = 0.6
700 / 1000 = 0.7
800 / 1000 = 0.8
900 / 1000 = 0.9
Number of items: 1000
Index dimension: 100
Metric : angular
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# =============================================================
# 3. Build index
# =============================================================
idx.build(10)
print("Trees:", idx.get_n_trees())
print("Memory usage:", idx.memory_usage(), "bytes")
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
# help(idx.build)
Trees: 10
Memory usage: 543076 bytes
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 543076, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.5179176330566406}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
idx.unbuild()
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 0}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
idx.build(10)
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 543076, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.5179176330566406}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# =============================================================
# 1. Construction
# =============================================================
idx = Index(0, metric="angular")
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
Index dimension: 0
Metric : angular
{'f': 0, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 0, 'n_trees': 0}
Annoy(**{'f': 0, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# =============================================================
# 2. Add items
# =============================================================
f=100
n=1000
for i in range(n):
if(i % (n//10) == 0): print(f"{i} / {n} = {1.0 * i / n}")
# v = []
# for z in range(f):
# v.append(random.gauss(0, 1))
v = [random.gauss(0, 1) for _ in range(f)]
idx.add_item(i, v)
print("Number of items:", idx.get_n_items())
print("Index dimension:", idx.f)
print("Metric :", idx.metric)
print(idx)
0 / 1000 = 0.0
100 / 1000 = 0.1
200 / 1000 = 0.2
300 / 1000 = 0.3
400 / 1000 = 0.4
500 / 1000 = 0.5
600 / 1000 = 0.6
700 / 1000 = 0.7
800 / 1000 = 0.8
900 / 1000 = 0.9
Number of items: 1000
Index dimension: 100
Metric : angular
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# =============================================================
# 3. Build index
# =============================================================
idx.build(10)
print("Trees:", idx.get_n_trees())
print("Memory usage:", idx.memory_usage(), "bytes")
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
# help(idx.get_n_trees)
Trees: 10
Memory usage: 611056 bytes
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 611056, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.5827484130859375}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# =============================================================
# 4. Query — return
# =============================================================
res = idx.get_nns_by_item(
0,
5,
# search_k = -1,
include_distances=True,
)
print(res)
([0, 762, 535, 864, 306], [0.00014125133748166263, 1.2786411046981812, 1.282088041305542, 1.2963494062423706, 1.3046419620513916])
# =============================================================
# 8. Query using vector
# =============================================================
res2 = idx.get_nns_by_vector(
[random.gauss(0, 1) for _ in range(f)],
5,
include_distances=True
)
print("\nQuery by vector:", res2)
Query by vector: ([566, 336, 695, 237, 408], [1.2055667638778687, 1.2275598049163818, 1.243502140045166, 1.2670350074768066, 1.2830111980438232])
# =============================================================
# 9. Low-level (non-result) mode
# =============================================================
items = idx.get_nns_by_item(0, 2, include_distances=False)
print("\nLow-level items only:", items)
items_low, d_low = idx.get_nns_by_item(0, 2, include_distances=True)
print("Low-level tuple return:", items_low, d_low)
Low-level items only: [0, 762]
Low-level tuple return: [0, 762] [0.00014125133748166263, 1.2786411046981812]
# =============================================================
# 10. Persistence
# =============================================================
print("\n=== Saving with binary annoy ===")
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
idx.save("annoy_test_2.annoy")
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
print("Loading...")
idx2 = Index(100, metric='angular').load("annoy_test_2.annoy")
print("Loaded index:", idx2)
=== Saving with binary annoy ===
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 611056, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.5827484130859375}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 543076, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.5179176330566406}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
Loading...
Loaded index: Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
import joblib
joblib.dump(idx2, "test.joblib")
a = joblib.load("test.joblib")
a
({'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 543076, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.5179176330566406}, 1000, 10)
np.array_equal(a.get_item_vector(0), idx2.get_item_vector(0))
True
np.array_equal(a.get_item_vector(0), idx.get_item_vector(0))
True
# =============================================================
# 11. Raw serialize / deserialize
# =============================================================
print("\n=== Raw serialize ===")
buf = idx.serialize()
new_idx = Index(100, metric='angular')
new_idx.deserialize(buf)
print("Deserialized index n_items:", new_idx.get_n_items())
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
=== Raw serialize ===
Deserialized index n_items: 1000
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 1000, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 543076, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.5179176330566406}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
idx.unload()
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 0, 'n_trees': 0}
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# idx.build(10)
idx.load("annoy_test_2.annoy")
print(idx)
type(idx)
Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
# joblib
import joblib
joblib.dump(idx, "test.joblib"), joblib.load("test.joblib")
(['test.joblib'], Annoy(**{'f': 100, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': 'annoy_test_2.annoy', 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0}))
from scikitplot import annoy as a
f = 10
idx = a.AnnoyIndex(f, "angular")
# Distinct non-zero content so we can see mismatches clearly
for i in range(20):
idx.add_item(i, [float(i)] * f)
idx.build(10)
type(idx)
from scikitplot import annoy as a
# Legacy Support
idx = a.Index.from_low_level(idx)
import joblib
joblib.dump(idx, "test.joblib")
type(idx)
print(idx.info())
print(idx)
idx
{'f': 10, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0, 'n_items': 20, 'n_trees': 10, 'memory_usage_byte': 4220, 'memory_usage_mib': 0.004024505615234375}
Annoy(**{'f': 10, 'metric': 'angular', 'n_neighbors': 5, 'on_disk_path': None, 'prefault': False, 'seed': None, 'verbose': None, 'schema_version': 0})
idx.get_nns_by_item(0, 10), len(idx.get_item_vector(0))
([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], 10)
import random
from scikitplot.utils._time import Timer
n, f = 1_000_000, 10
X = [[random.gauss(0, 1) for _ in range(f)] for _ in range(n)]
q = [[random.gauss(0, 1) for _ in range(f)]]
# idx = Index().fit(X, feature_names=map("feature_{}".format, range(0,10)))
idx = Index().fit(X, feature_names=map("col_{}".format, range(0,10)))
idx
idx.feature_names_in_
('col_0', 'col_1', 'col_2', 'col_3', 'col_4', 'col_5', 'col_6', 'col_7', 'col_8', 'col_9')
idx.transform(X[:5], include_distances=True, return_labels=True)
([[[0.2995162308216095, 0.26872411370277405, -0.31986403465270996, 0.40183380246162415, -0.38237830996513367, 0.9011735916137695, 0.7422892451286316, 0.8437517285346985, 1.3799339532852173, -0.06174032390117645], [0.3315776586532593, 0.1875527799129486, -0.8046607375144958, 0.3848173916339874, -0.5218529105186462, 0.9577100872993469, 0.6407361626625061, 0.6109951138496399, 1.6533797979354858, -0.14335046708583832], [1.066840648651123, 0.5097151398658752, -0.02644050307571888, 0.5691455006599426, -0.6068020462989807, 1.3134701251983643, 0.8040322065353394, 1.5368680953979492, 1.9145973920822144, -0.1704350709915161], [0.5550230741500854, 0.1936453878879547, -0.6877626776695251, 0.3667159378528595, -1.054802417755127, 1.2736949920654297, 0.7120872139930725, 0.9665201306343079, 1.589842438697815, 0.11769255250692368], [0.6585002541542053, 1.2284033298492432, -0.5905928611755371, 0.8687102198600769, -0.38249245285987854, 1.7344026565551758, 2.142791271209717, 1.7588355541229248, 2.0976037979125977, 0.07778248935937881]], [[-0.4028843939304352, 0.6818151473999023, -1.117720365524292, 1.0333377122879028, 0.1900119036436081, -0.8227489590644836, 0.7598976492881775, 0.5180985927581787, 0.3719368278980255, 1.6910221576690674], [-0.27890557050704956, 0.46175551414489746, -0.9916201829910278, 1.0096960067749023, 0.4043457806110382, -0.5705316066741943, 0.25394734740257263, 0.8305667638778687, 0.05997063219547272, 1.143517255783081], [-0.39958956837654114, 0.2775285840034485, -0.9795499444007874, 2.0570271015167236, 0.19776058197021484, -0.7846500277519226, 0.5791918635368347, 0.7596640586853027, 0.3216345012187958, 2.0459976196289062], [-0.6214601397514343, 0.3489237129688263, -1.188614010810852, 1.082640290260315, -0.1073702871799469, -0.48028117418289185, 0.4220775365829468, 1.1602388620376587, 0.5457847118377686, 2.1855993270874023], [-0.47564759850502014, 0.5954586863517761, -0.645365834236145, 0.6735963225364685, -0.003365585347637534, -0.7522469162940979, 0.4252465069293976, 0.868837296962738, -0.06324155628681183, 1.0693514347076416]], [[-0.21217121183872223, 0.2056313157081604, 0.722652018070221, 0.8762103319168091, 0.6707500219345093, -1.6379401683807373, 0.9332223534584045, -0.5422225594520569, -1.1026482582092285, 0.056520331650972366], [-0.2671450972557068, 0.30244287848472595, 0.6430985927581787, 0.5063324570655823, 0.7001524567604065, -2.2902638912200928, 1.2434182167053223, -0.9914654493331909, -1.3870468139648438, -0.19567644596099854], [-0.4286768138408661, 0.7249663472175598, 0.6372804641723633, 1.19240403175354, 1.4679796695709229, -2.310258150100708, 1.4233965873718262, -0.17894130945205688, -1.9173343181610107, -0.042759768664836884], [-0.6377572417259216, -0.5511672496795654, 0.5751820206642151, 1.4192023277282715, 0.5922985672950745, -2.668642997741699, 1.5364527702331543, -0.8178994655609131, -1.6896406412124634, 0.10657071322202682], [-0.09657622873783112, -0.03825854882597923, 0.19272591173648834, 1.1368770599365234, 0.6961694955825806, -1.9996322393417358, 0.7544685006141663, -0.9075682163238525, -1.4941128492355347, -0.3546978831291199]], [[1.8360724449157715, -1.7788029909133911, -1.0985404253005981, -1.2299158573150635, -0.4852966070175171, 0.22859908640384674, -0.03444309160113335, -0.34960466623306274, -0.2747590243816376, 0.1640910655260086], [2.132922649383545, -1.8067975044250488, -0.5985732078552246, -1.4354743957519531, -0.6862561702728271, -0.055050190538167953, -0.20438416302204132, -0.10576765984296799, -0.18300966918468475, 0.0332980640232563], [2.028416633605957, -2.3481366634368896, -0.8087594509124756, -0.9565438032150269, -1.0041019916534424, 0.3109251856803894, -0.20483307540416718, -0.5396076440811157, -0.5114067196846008, 0.5764236450195312], [1.1669689416885376, -1.1882712841033936, -1.2006605863571167, -0.9844658970832825, -0.35999438166618347, 0.1763678342103958, -0.16189533472061157, -0.22041620314121246, -0.4420163631439209, -0.25835075974464417], [1.376590609550476, -1.4930306673049927, -0.77528977394104, -0.40215086936950684, -0.7235462069511414, -0.08473818749189377, -0.25408416986465454, -0.28316476941108704, -0.07844149321317673, 0.02014928311109543]], [[0.38939982652664185, -0.7888681292533875, 0.21797947585582733, -0.39556416869163513, 0.09195032715797424, -0.45746126770973206, 0.7257154583930969, 0.163970485329628, 0.3641418516635895, 0.2510545551776886], [1.57913339138031, -2.1115193367004395, 0.8659923672676086, -1.4170335531234741, 0.31213846802711487, -1.1963188648223877, 1.6555734872817993, 0.32366394996643066, 0.7790639996528625, 0.7397186160087585], [0.3067862093448639, -1.1996709108352661, 0.2953212559223175, -0.8477502465248108, -0.09012967348098755, -0.589461088180542, 1.2440359592437744, 0.19568035006523132, 0.5365380048751831, 0.5055891871452332], [1.0569108724594116, -1.1905972957611084, 0.2124386429786682, -0.611705482006073, -0.0573427639901638, -1.1755845546722412, 1.216412901878357, 0.34951576590538025, 0.6942406296730042, 0.12841904163360596], [0.5571768283843994, -1.5110305547714233, 0.44180983304977417, -0.579093873500824, -0.3039686977863312, -0.5685702562332153, 1.7404046058654785, 0.043175242841243744, 0.5812414884567261, 0.32155993580818176]]], [[0.00040781544521450996, 0.26271525025367737, 0.2775248885154724, 0.2870346009731293, 0.2919205129146576], [0.0, 0.32887229323387146, 0.3404887020587921, 0.34077882766723633, 0.35751163959503174], [0.0004033695731777698, 0.24741443991661072, 0.2679187059402466, 0.28913918137550354, 0.31792834401130676], [0.0003501259780023247, 0.2397470772266388, 0.26940304040908813, 0.2777542769908905, 0.3216817080974579], [0.00044628308387473226, 0.20473265647888184, 0.22700366377830505, 0.2834739089012146, 0.2978987991809845]], [[None, None, None, None, None], [None, None, None, None, None], [None, None, None, None, None], [None, None, None, None, None], [None, None, None, None, None]])
with Timer("set_params"):
for m in ["angular", "l1", "l2", ".", "hamming"]:
idx = Index().set_params(metric=m).fit(X)
print(m, idx.transform(q))
angular [[[-0.576092004776001, -1.1014655828475952, 1.5072448253631592, -0.37987226247787476, -0.12107884138822556, -0.16090495884418488, -0.9599498510360718, 0.6443582773208618, 0.7830631136894226, 0.1322690099477768], [0.16887520253658295, -1.431685447692871, 2.3795950412750244, -0.07162338495254517, -0.12440761923789978, -0.39936673641204834, -1.4955497980117798, 0.8629574179649353, 0.6653525233268738, -0.2006359100341797], [-0.14904215931892395, -1.9222668409347534, 2.399625778198242, -0.568252444267273, 0.47048714756965637, -0.5003377199172974, -1.3439618349075317, 1.420609951019287, 1.4913909435272217, -0.13222387433052063], [-0.5908904075622559, -1.0413066148757935, 1.2289979457855225, -0.1970331072807312, -0.20727333426475525, -0.8007806539535522, -1.012205719947815, 0.8112825751304626, 0.48573213815689087, -0.43459779024124146], [-0.38383179903030396, -0.8648300766944885, 1.7170730829238892, 0.30777204036712646, 0.4790739119052887, -0.9346842169761658, -0.9029712677001953, 1.050656795501709, 0.6370121240615845, -0.5025318264961243]]]
l1 [[[0.16887520253658295, -1.431685447692871, 2.3795950412750244, -0.07162338495254517, -0.12440761923789978, -0.39936673641204834, -1.4955497980117798, 0.8629574179649353, 0.6653525233268738, -0.2006359100341797], [-0.5415041446685791, -1.1800884008407593, 1.529439091682434, 0.11952074617147446, -0.2929523289203644, -0.5609923601150513, -0.9184246063232422, 1.3177564144134521, 1.6426866054534912, 0.32133588194847107], [-0.38383179903030396, -0.8648300766944885, 1.7170730829238892, 0.30777204036712646, 0.4790739119052887, -0.9346842169761658, -0.9029712677001953, 1.050656795501709, 0.6370121240615845, -0.5025318264961243], [-0.25011304020881653, -0.8852328062057495, 1.9768023490905762, -0.26991376280784607, -0.39031121134757996, -0.5427191853523254, -1.340255618095398, 0.3214011788368225, 0.6619998216629028, -0.03233140707015991], [-0.4270615875720978, -1.5546542406082153, 1.813949704170227, -0.2853894829750061, 0.43189895153045654, -0.4212631285190582, -0.8940620422363281, 0.34188783168792725, 1.3183560371398926, -0.31580230593681335]]]
l2 [[[-0.6069902777671814, -1.5303187370300293, 1.7485501766204834, 0.09983374923467636, -0.2737273573875427, -0.4870619773864746, -0.857934296131134, 0.7189533114433289, 0.4311307370662689, 0.388454407453537], [-0.5928851366043091, -1.1504853963851929, 1.882880687713623, -0.17135651409626007, -0.2929040789604187, 0.17471130192279816, -1.4388010501861572, 0.6688973307609558, 0.8859867453575134, 0.00527344923466444], [-0.576092004776001, -1.1014655828475952, 1.5072448253631592, -0.37987226247787476, -0.12107884138822556, -0.16090495884418488, -0.9599498510360718, 0.6443582773208618, 0.7830631136894226, 0.1322690099477768], [-0.8246579170227051, -1.5498437881469727, 1.722296118736267, 0.12505893409252167, -0.5007220506668091, -0.5869333148002625, -1.1538058519363403, 0.8996411561965942, 0.046726711094379425, -0.06863833218812943], [-0.25011304020881653, -0.8852328062057495, 1.9768023490905762, -0.26991376280784607, -0.39031121134757996, -0.5427191853523254, -1.340255618095398, 0.3214011788368225, 0.6619998216629028, -0.03233140707015991]]]
. [[[-0.7904490232467651, -2.213721990585327, 4.029660224914551, -0.13080434501171112, -0.3086875379085541, -2.5304341316223145, -0.5008127689361572, 0.9512909054756165, 0.5966078639030457, 0.09866325557231903], [-1.1499366760253906, -1.3602036237716675, 2.739813804626465, -0.02609434723854065, 1.4179996252059937, -0.8871392607688904, -1.1483855247497559, 2.639958143234253, 1.8300042152404785, -0.17696726322174072], [-0.16006967425346375, -2.0737016201019287, 3.058436632156372, -0.14764907956123352, 0.9704813361167908, 0.5407483577728271, -1.440893292427063, 1.7912302017211914, 1.1538074016571045, 0.28450268507003784], [-1.3420894145965576, -0.9585272669792175, 1.9888936281204224, 0.24738776683807373, -0.535808265209198, -0.17154152691364288, -1.9633593559265137, 2.0907199382781982, 2.229039192199707, -0.8974798917770386], [-0.39104288816452026, -1.0270168781280518, 2.9437875747680664, 1.9474108219146729, 0.7511434555053711, -2.6756348609924316, -1.4545743465423584, 0.9195820093154907, 0.8578388094902039, 0.20662806928157806]]]
hamming [[[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0]]]
with Timer("rebuild"):
base = Index(metric="l2").fit(X)
for m in ["angular", "l1", "l2", "dot", "hamming"]:
idx_m = base.rebuild(metric=m) # rebuild-from-index
print(m, idx_m.transform(q)) # no .fit(X) here
angular [[[-0.576092004776001, -1.1014655828475952, 1.5072448253631592, -0.37987226247787476, -0.12107884138822556, -0.16090495884418488, -0.9599498510360718, 0.6443582773208618, 0.7830631136894226, 0.1322690099477768], [0.16887520253658295, -1.431685447692871, 2.3795950412750244, -0.07162338495254517, -0.12440761923789978, -0.39936673641204834, -1.4955497980117798, 0.8629574179649353, 0.6653525233268738, -0.2006359100341797], [-0.14904215931892395, -1.9222668409347534, 2.399625778198242, -0.568252444267273, 0.47048714756965637, -0.5003377199172974, -1.3439618349075317, 1.420609951019287, 1.4913909435272217, -0.13222387433052063], [-0.5908904075622559, -1.0413066148757935, 1.2289979457855225, -0.1970331072807312, -0.20727333426475525, -0.8007806539535522, -1.012205719947815, 0.8112825751304626, 0.48573213815689087, -0.43459779024124146], [-0.38383179903030396, -0.8648300766944885, 1.7170730829238892, 0.30777204036712646, 0.4790739119052887, -0.9346842169761658, -0.9029712677001953, 1.050656795501709, 0.6370121240615845, -0.5025318264961243]]]
l1 [[[0.16887520253658295, -1.431685447692871, 2.3795950412750244, -0.07162338495254517, -0.12440761923789978, -0.39936673641204834, -1.4955497980117798, 0.8629574179649353, 0.6653525233268738, -0.2006359100341797], [-0.5415041446685791, -1.1800884008407593, 1.529439091682434, 0.11952074617147446, -0.2929523289203644, -0.5609923601150513, -0.9184246063232422, 1.3177564144134521, 1.6426866054534912, 0.32133588194847107], [-0.38383179903030396, -0.8648300766944885, 1.7170730829238892, 0.30777204036712646, 0.4790739119052887, -0.9346842169761658, -0.9029712677001953, 1.050656795501709, 0.6370121240615845, -0.5025318264961243], [-0.25011304020881653, -0.8852328062057495, 1.9768023490905762, -0.26991376280784607, -0.39031121134757996, -0.5427191853523254, -1.340255618095398, 0.3214011788368225, 0.6619998216629028, -0.03233140707015991], [-0.4270615875720978, -1.5546542406082153, 1.813949704170227, -0.2853894829750061, 0.43189895153045654, -0.4212631285190582, -0.8940620422363281, 0.34188783168792725, 1.3183560371398926, -0.31580230593681335]]]
l2 [[[-0.6069902777671814, -1.5303187370300293, 1.7485501766204834, 0.09983374923467636, -0.2737273573875427, -0.4870619773864746, -0.857934296131134, 0.7189533114433289, 0.4311307370662689, 0.388454407453537], [-0.5928851366043091, -1.1504853963851929, 1.882880687713623, -0.17135651409626007, -0.2929040789604187, 0.17471130192279816, -1.4388010501861572, 0.6688973307609558, 0.8859867453575134, 0.00527344923466444], [-0.576092004776001, -1.1014655828475952, 1.5072448253631592, -0.37987226247787476, -0.12107884138822556, -0.16090495884418488, -0.9599498510360718, 0.6443582773208618, 0.7830631136894226, 0.1322690099477768], [-0.8246579170227051, -1.5498437881469727, 1.722296118736267, 0.12505893409252167, -0.5007220506668091, -0.5869333148002625, -1.1538058519363403, 0.8996411561965942, 0.046726711094379425, -0.06863833218812943], [-0.25011304020881653, -0.8852328062057495, 1.9768023490905762, -0.26991376280784607, -0.39031121134757996, -0.5427191853523254, -1.340255618095398, 0.3214011788368225, 0.6619998216629028, -0.03233140707015991]]]
dot [[[-0.7904490232467651, -2.213721990585327, 4.029660224914551, -0.13080434501171112, -0.3086875379085541, -2.5304341316223145, -0.5008127689361572, 0.9512909054756165, 0.5966078639030457, 0.09866325557231903], [-1.1499366760253906, -1.3602036237716675, 2.739813804626465, -0.02609434723854065, 1.4179996252059937, -0.8871392607688904, -1.1483855247497559, 2.639958143234253, 1.8300042152404785, -0.17696726322174072], [-0.16006967425346375, -2.0737016201019287, 3.058436632156372, -0.14764907956123352, 0.9704813361167908, 0.5407483577728271, -1.440893292427063, 1.7912302017211914, 1.1538074016571045, 0.28450268507003784], [-1.3420894145965576, -0.9585272669792175, 1.9888936281204224, 0.24738776683807373, -0.535808265209198, -0.17154152691364288, -1.9633593559265137, 2.0907199382781982, 2.229039192199707, -0.8974798917770386], [-0.39104288816452026, -1.0270168781280518, 2.9437875747680664, 1.9474108219146729, 0.7511434555053711, -2.6756348609924316, -1.4545743465423584, 0.9195820093154907, 0.8578388094902039, 0.20662806928157806]]]
hamming [[[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0]]]
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 22.744 seconds)
Related examples