plot_lift#
- scikitplot.deciles.plot_lift(y_true, y_probas, *, class_names=None, multi_class=None, class_index=1, to_plot_class_index=None, title='Lift Curves', ax=None, fig=None, figsize=None, title_fontsize='large', text_fontsize='medium', cmap=None, show_labels=True, plot_micro=False, plot_macro=False, **kwargs)#
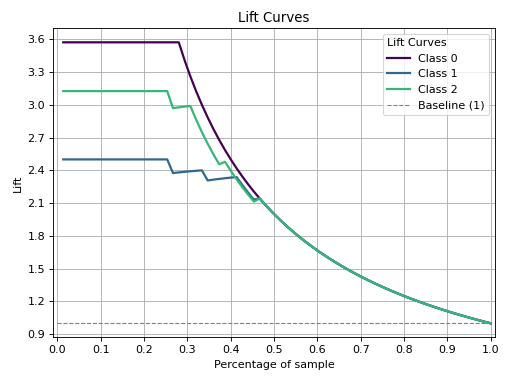
Generate a Lift Curve from true labels and predicted probabilities.
The lift curve evaluates the performance of a classifier by comparing the lift (or improvement) achieved by using the model compared to random guessing. The implementation supports binary classification directly and multiclass classification through One-vs-Rest (OVR) or multinomial strategies.
- Parameters:
y_true (array-like of shape (n_samples,)) – Ground truth (correct) target values.
y_probas (array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_classes)) – Predicted probabilities for each class or only target class probabilities. If 1D, it is treated as probabilities for the positive class in binary or multiclass classification with the
class_index.class_names (list of str, optional, default=None) – List of class names for the legend. Order should match the order of classes in
y_probas.multi_class ({'ovr', 'multinomial', None}, optional, default=None) – Strategy for handling multiclass classification: - ‘ovr’: One-vs-Rest, plotting binary problems for each class. - ‘multinomial’ or None: Multinomial plot for the entire probability distribution.
class_index (int, optional, default=1) – Index of the class of interest for multi-class classification. Ignored for binary classification.
to_plot_class_index (list-like, optional, default=None) – Specific classes to plot. If a given class does not exist, it will be ignored. If None, all classes are plotted. e.g. [0, ‘cold’]
title (str, default='Lift Curves') – Title of the plot.
ax (list of matplotlib.axes.Axes, optional, default=None) – The axis to plot the figure on. If None is passed in the current axes will be used (or generated if required). Axes like
fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)orplt.gca()fig (matplotlib.pyplot.figure, optional, default: None) –
The figure to plot the Visualizer on. If None is passed in the current plot will be used (or generated if required).
Added in version 0.3.9.
figsize (tuple of int, optional, default=None) – Size of the figure (width, height) in inches.
title_fontsize (str or int, optional, default='large') – Font size for the plot title.
text_fontsize (str or int, optional, default='medium') – Font size for the text in the plot.
cmap (None, str or matplotlib.colors.Colormap, optional, default=None) – Colormap used for plotting. Options include ‘viridis’, ‘PiYG’, ‘plasma’, ‘inferno’, ‘nipy_spectral’, etc. See Matplotlib Colormap documentation for available choices. - https://matplotlib.org/stable/users/explain/colors/index.html - plt.colormaps() - plt.get_cmap() # None == ‘viridis’
show_labels (bool, optional, default=True) –
Whether to display the legend labels.
Added in version 0.3.9.
plot_micro (bool, optional, default=False) – Whether to plot the micro-average Lift curve.
plot_macro (bool, optional, default=False) – Whether to plot the macro-average Lift curve.
show_labels –
Whether to display the legend labels.
Added in version 0.3.9.
- Returns:
The axes with the plotted lift curves.
- Return type:
Notes
The implementation is specific to binary classification. For multiclass problems, the ‘ovr’ or ‘multinomial’ strategies can be used. When
multi_class='ovr', the plot focuses on the specified class (class_index).See also
plot_lift_decile_wiseGenerates the Decile-wise Lift Plot from labels and probabilities.
References
[1] http://www2.cs.uregina.ca/~dbd/cs831/notes/lift_chart/lift_chart.html
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris as data_3_classes >>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> import scikitplot as skplt >>> X, y = data_3_classes(return_X_y=True, as_frame=False) >>> X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=0) >>> model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=int(1e5), random_state=0).fit(X_train, y_train) >>> y_probas = model.predict_proba(X_val) >>> skplt.deciles.plot_lift( >>> y_val, y_probas, >>> );
(
Source code,png)