Kiss32Random#
- class scikitplot.random.Kiss32Random(int seed: int | None = None)[source]#
32-bit KISS RNG with complete serialization support.
Period: ~2^121 (suitable for <16M data points)
- Parameters:
- seedint or None, optional
Random seed. If None, uses default seed.
- Attributes:
- default_seedint
Default seed value (123456789)
seedintKiss32Random.seed: int
- lockthreading.RLock
Thread lock (for shared access)
See also
Kiss64Random64-bit version for larger datasets
KissRandomFactory function for auto-detecting
KissSeedSequenceSeed sequence for initialization
KissBitGeneratorNumPy-compatible bit generator
KissGeneratorHigh-level generator using this BitGenerator
KissRandomStateInherites from KissGenerator
default_rngConvenience function to create generator
Notes
Period: approximately 2^121
Not cryptographically secure
Suitable for up to ~2^24 data points
For larger datasets, use Kiss64Random
Thread-safe via context manager
Deterministic: same seed → same sequence
Complete pickle/JSON support
The KISS32 algorithm combines: - Linear Congruential Generator (LCG) - Xorshift generator - Multiply-With-Carry (MWC) generator
References
[1]Marsaglia, G. (1999). “Random Number Generators.”
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> rng.kiss() # Random uint32 >>> >>> # Context manager (thread-safe) >>> with rng: ... value = rng.kiss() >>> >>> # Serialization >>> import pickle >>> restored = pickle.loads(pickle.dumps(rng))
- default_seed = 123456789#
- classmethod deserialize(cls, data)#
Deserialize from dict.
- Parameters:
- datadict
Serialized state
- Returns:
- Kiss32Random
Restored instance
Examples
>>> import json >>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> json_str = json.dumps(rng.serialize()) >>> data = json.loads(json_str) >>> restored = Kiss32Random.deserialize(data)
- flip(self) int#
Generate random binary value (0 or 1).
- Returns:
- int
Either 0 or 1 with equal probability
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> rng.flip() in {0, 1} True
Coin flip simulation:
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(123) >>> flips = [rng.flip() for _ in range(1000)] >>> abs(sum(flips) - 500) < 50 # Approximately 50% heads True
- classmethod from_dict(cls, data)#
Alias for deserialize().
- static get_default_seed() int#
Get default seed value.
- Returns:
- int
Default seed (123456789)
- Return type:
Examples
>>> Kiss32Random.get_default_seed() 123456789
- get_params(self, deep=True)#
Get parameters (sklearn-style).
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
Unused, for sklearn compatibility
- Returns:
- dict
Constructor parameters
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> params = rng.get_params() >>> print(params) {'seed': 42}
- get_state(self)#
Get state dictionary.
- Returns:
- dict
Complete state
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> state = rng.get_state() >>> print(state["seed"]) 42
- index(self, size_t n) size_t#
Generate random index in range [0, n-1].
- Parameters:
- nint
Upper bound (exclusive). Must be >= 0.
- Returns:
- int
Random integer in [0, n-1], or 0 if n==0
- Raises:
- ValueError
If n < 0
- TypeError
If n not an integer
Notes
Handles n==0 gracefully (returns 0)
Uses modulo for simplicity (suitable for non-crypto use)
Slight modulo bias exists but negligible for non-crypto applications
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> idx = rng.index(100) >>> 0 <= idx < 100 True
Array indexing:
>>> import numpy as np >>> arr = np.arange(100, 200) >>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> random_element = arr[rng.index(len(arr))]
- kiss(self) uint32_t#
Generate next random 32-bit unsigned integer.
- Returns:
- int
Random value in [0, 2^32-1]
Notes
This is the core RNG method. Other methods (flip, index) build on it.
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> value = rng.kiss() >>> 0 <= value < 2**32 True
- lock#
!! processed by numpydoc !!
- static normalize_seed(int seed: int) int#
Normalize seed to valid non-zero value.
- Parameters:
- seedint
User-provided seed
- Returns:
- int
Normalized seed (original if non-zero, else default_seed)
- Parameters:
seed (int)
- Return type:
Notes
Maps seed==0 to default_seed to avoid degenerate RNG states.
Examples
>>> Kiss32Random.normalize_seed(42) 42 >>> Kiss32Random.normalize_seed(0) 123456789
- reset(self, int seed: int) None#
Reset RNG state with new seed.
- Parameters:
- seedint
New seed value
- Raises:
- ValueError
If seed out of range
- Parameters:
seed (int)
- Return type:
None
Notes
Fully resets all internal state variables.
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> values1 = [rng.kiss() for _ in range(5)] >>> rng.reset(42) >>> values2 = [rng.kiss() for _ in range(5)] >>> values1 == values2 True
- reset_default(self) None#
Reset to default seed.
Equivalent to reset(default_seed).
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random() >>> rng.reset_default() >>> rng.seed == Kiss32Random.default_seed True
- Return type:
None
- seed#
int
Get current seed value.
- Returns:
- int
Current seed
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> rng.seed 42
- Type:
- serialize(self)#
Serialize to JSON-compatible dict.
- Returns:
- dict
JSON-serializable state
Examples
>>> import json >>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> data = rng.serialize() >>> json_str = json.dumps(data)
- set_params(self, **params)#
Set parameters (sklearn-style).
- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Parameters to set
- Returns:
- self
For chaining
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random(42) >>> rng.set_params(seed=123) >>> print(rng.seed) 123
- set_seed(self, int seed: int) None#
Set new seed (alias for reset).
- Parameters:
- seedint
New seed value
- Parameters:
seed (int)
- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> rng = Kiss32Random() >>> rng.set_seed(42)
- set_state(self, state)#
Set state from dictionary.
- Parameters:
- statedict
State from get_state()
Examples
>>> rng1 = Kiss32Random(42) >>> state = rng1.get_state() >>> rng2 = Kiss32Random(0) >>> rng2.set_state(state)
- to_dict(self)#
Alias for serialize().
Gallery examples#
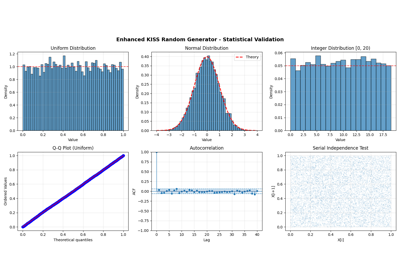
Enhanced KISS Random Generator - Complete Usage Examples
